Swimming
Swimming
Swimming is a popular sport for people with visual impairments at both the grassroots and high performance levels.
It is governed by World Para Swimming and competitions are held under their rules, which are in some cases modified from the International Swimming Federation (FINA) rules.
Swimming is a Paralympic sport with multiple events for athletes with visual impairments. World Para Swimming also organises world, regional and lower level competitions.
The sport is a regular fixture at the IBSA World Games where the largest programme of medal events for swimmers with visual impairments are showcased.
Swimmers compete in S11, S12 and S13 classes and are defined under the IBSA sight classifications of B1, B2 and B3.
- B1 and B2 athletes have the most severe visual impairments.
- B1 swimmers must wear darkened goggles and allowances are made in the rules for athletes who may be too close to a lane line to execute a stroke correctly, or who touch the lines in butterfly or breaststroke.

Other adaptations
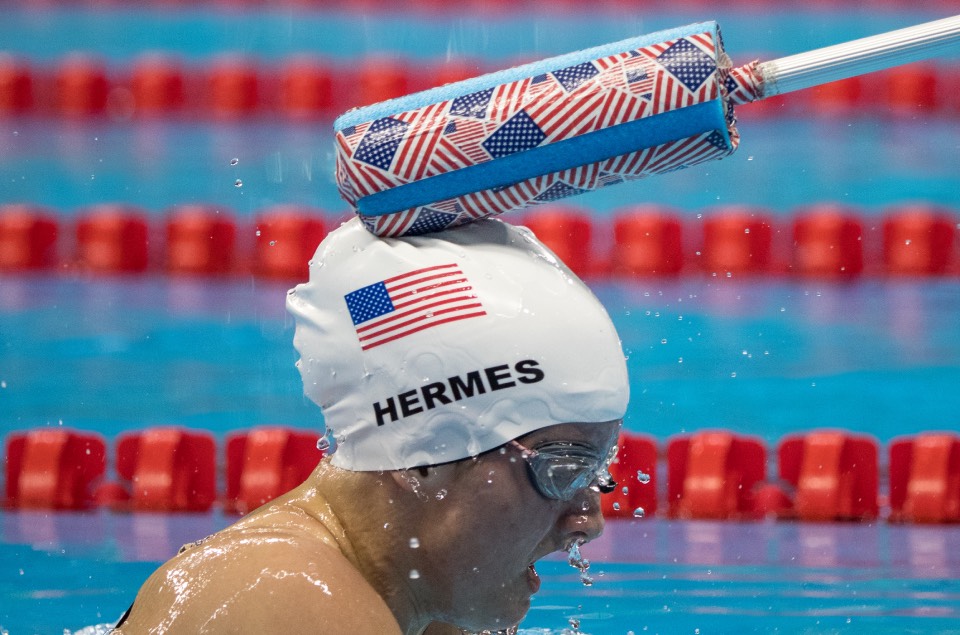
Swimmers with visual impairments may also make use of a ‘tapper’ which is perhaps one of the most iconic elements of Para swimming.
Tappers are experienced guides who are positioned at each end of the pool and use a rod with a firm foam tip to touch or tap the swimmer at the correct moment.
This method started in the 1980s as a way of letting a swimmer know that the end of the pool is coming. It was developed by Wilf and Audrey Strom and is now used by B1 and some B2 and B3 athletes.
Tappers must synchronize their tap with the swimmer’s stroke movement and momentum. This must happen at exactly the right time to enable the swimmer to approach at top speed. They must be without fear of crashing into the end of the pool in order to execute a racing turn without losing precious fractions of seconds in a race. A high level of trust is crucial.
In addition in relays featuring athletes with visual impairments, a coach may direct the takeovers if a swimmer cannot see their teammate approaching.
History
Para swimming is one of the original Paralympic sports, having featured at the first edition at Rome 1960.
The first swimmers with visual impairments competed at Toronto 1976.
Over the years those competing in S11, S12 and S13 classifications have become the quickest Para swimmers.
The world’s fastest Paralympian, Ukraine’s Maksym Veraksa, holds the current best in the men’s 50m freestyle S12 of 22.99 seconds.
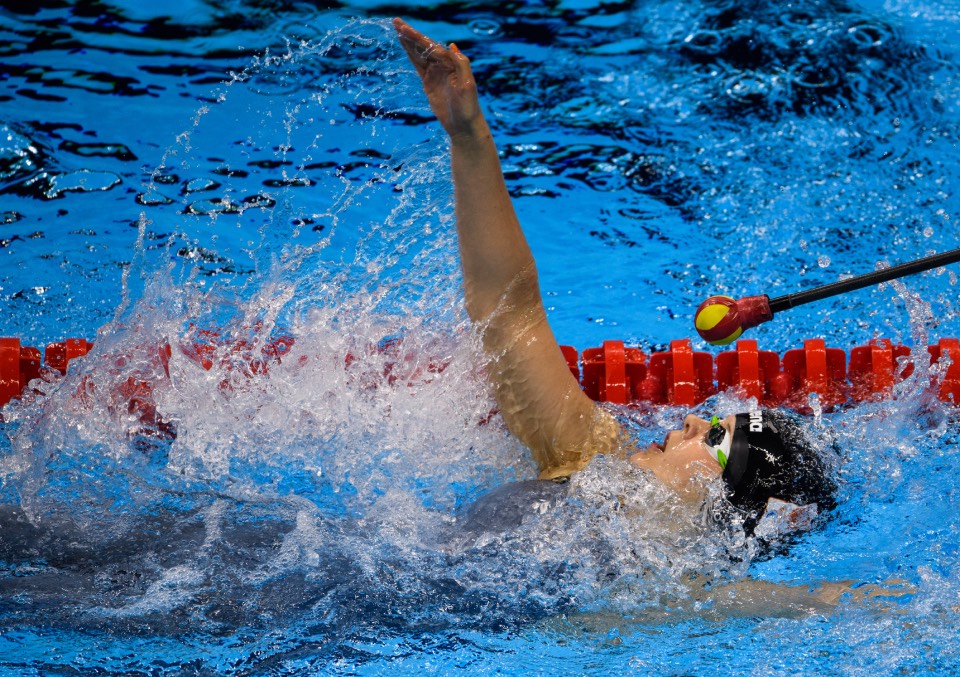
Historic results and records
IBSA Swimming Committee
IBSA helps to inform research into classification and to train classifiers for swimming. In addition the IBSA Swimming Committee helps to organise competitions and ensure that athletes with visual impairments are fairly represented at competitions around the world
Jane D. Blaine
Chairwoman
Hamid Sharifian
Member
